Bootstrap Form Elements
Overview
Bootstrap offers a number of form command looks, layout options, plus custom made elements for setting up a wide range of Bootstrap Form Field.
Forms offer the ideal system for having several comments from the website visitors of our web pages. In the case that it is actually a basic touch or else subscription form with simply just a couple of areas or else a highly developed and nicely thought examination the Bootstrap 4 structure got all things that is certainly required to accomplish the function and attain great responsive appearance.
By default located in the Bootstrap framework the form elements are designated to span the whole width of its own parent element-- this stuff gets accomplished by assigning the .form-control class. The commands and lebels really should be wrapped inside a parent element using the .form-group class for the very best spacing.
Bootstrap Form Template regulations
Bootstrap's form commands develop with regards to our Rebooted form looks along with classes.
Make use of these classes to opt in to their customed displays to get a additional consistent rendering around gadgets and browsers . The good example form listed here displays basic HTML form features which get updated styles from Bootstrap plus additional classes.
Always remember, due to the fact that Bootstrap utilizes the HTML5 doctype, all of the inputs must provide a type attribute.
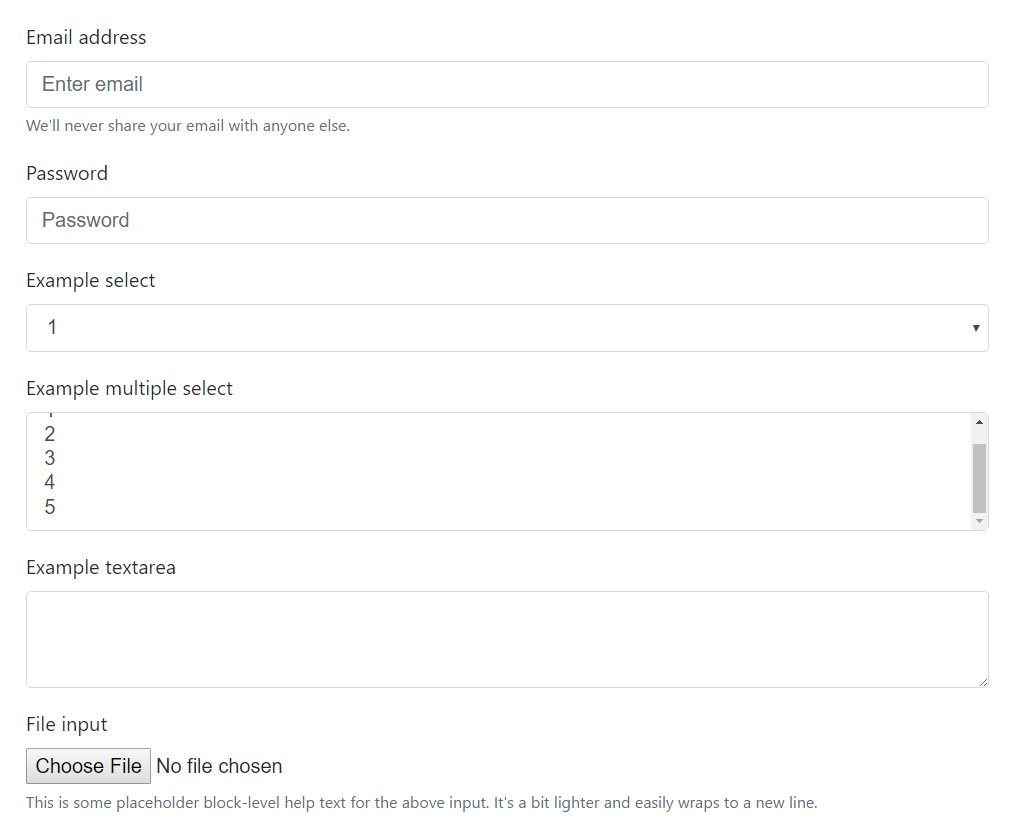
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter email">
<small id="emailHelp" class="form-text text-muted">We'll never share your email with anyone else.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect1">Example select</label>
<select class="form-control" id="exampleSelect1">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect2">Example multiple select</label>
<select multiple class="form-control" id="exampleSelect2">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleTextarea">Example textarea</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="exampleTextarea" rows="3"></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">File input</label>
<input type="file" class="form-control-file" id="exampleInputFile" aria-describedby="fileHelp">
<small id="fileHelp" class="form-text text-muted">This is some placeholder block-level help text for the above input. It's a bit lighter and easily wraps to a new line.</small>
</div>
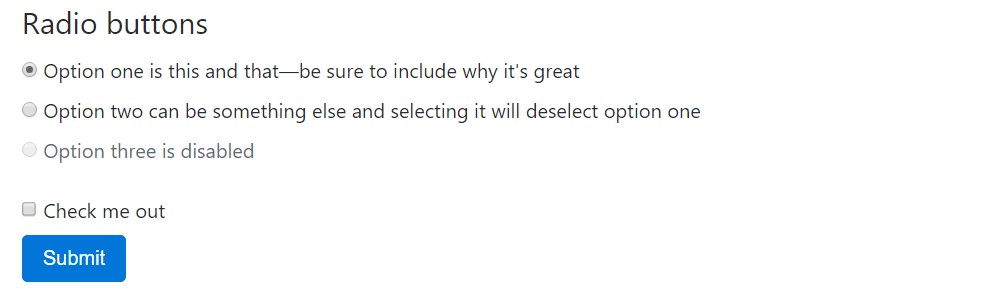
<fieldset class="form-group">
<legend>Radio buttons</legend>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input">
Check me out
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Here is a finished listing of the specific Bootstrap Form Elements regulations assisted by Bootstrap together with the classes that modify them. Special documents is offered for every group.
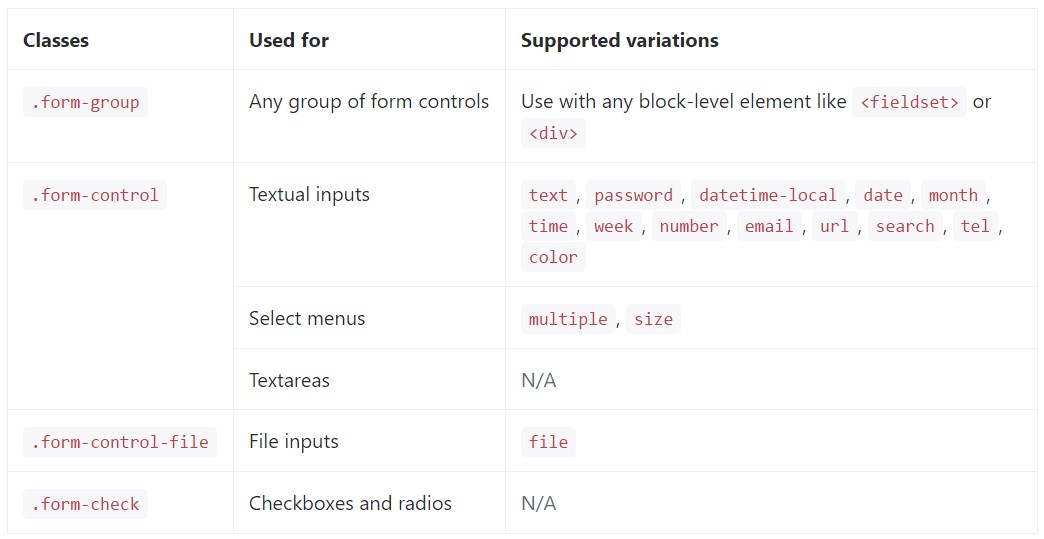
Textual inputs
Right here are the samples of .form-control related to each textual HTML5 <input> type.
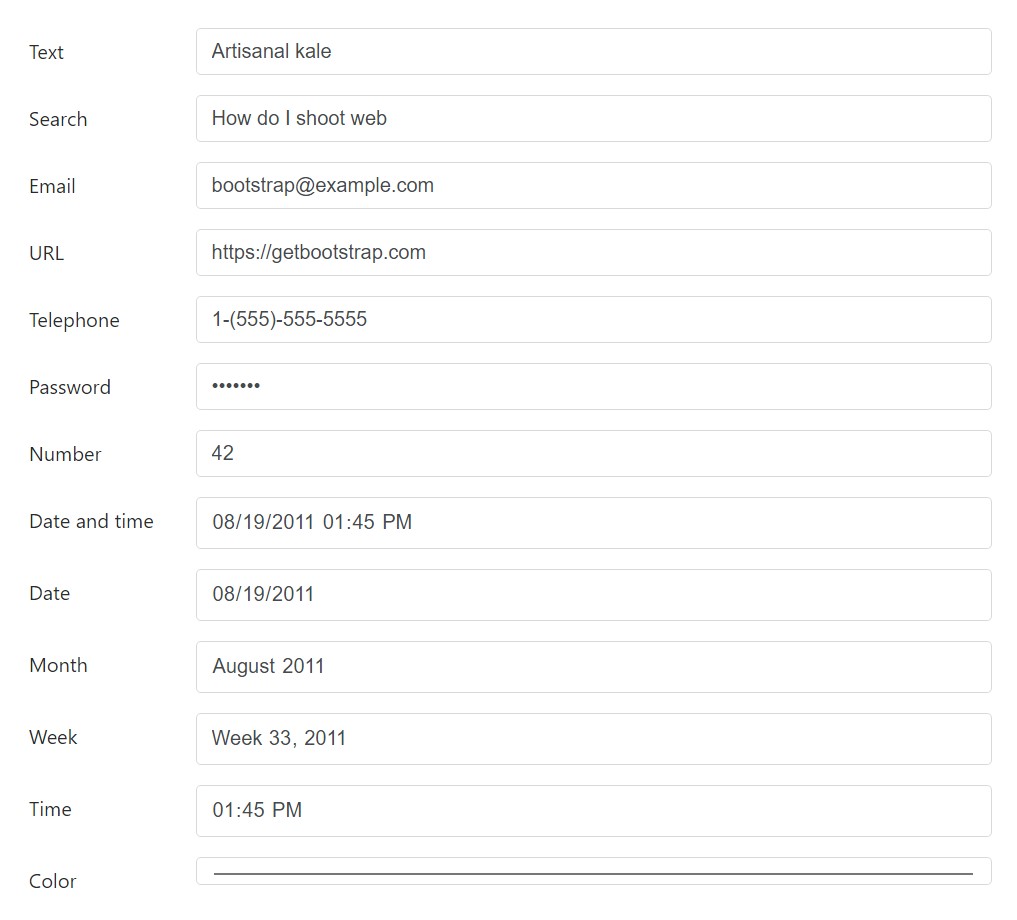
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-text-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Text</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="text" value="Artisanal kale" id="example-text-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-search-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Search</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="search" value="How do I shoot web" id="example-search-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-email-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="email" value="[email protected]" id="example-email-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-url-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">URL</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="url" value="https://getbootstrap.com" id="example-url-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-tel-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Telephone</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="tel" value="1-(555)-555-5555" id="example-tel-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-password-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="password" value="hunter2" id="example-password-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-number-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Number</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="number" value="42" id="example-number-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-datetime-local-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date and time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="datetime-local" value="2011-08-19T13:45:00" id="example-datetime-local-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-date-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="date" value="2011-08-19" id="example-date-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-month-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Month</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="month" value="2011-08" id="example-month-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-week-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Week</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="week" value="2011-W33" id="example-week-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-time-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="time" value="13:45:00" id="example-time-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-color-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Color</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="color" value="#563d7c" id="example-color-input">
</div>
</div>Form arrangements
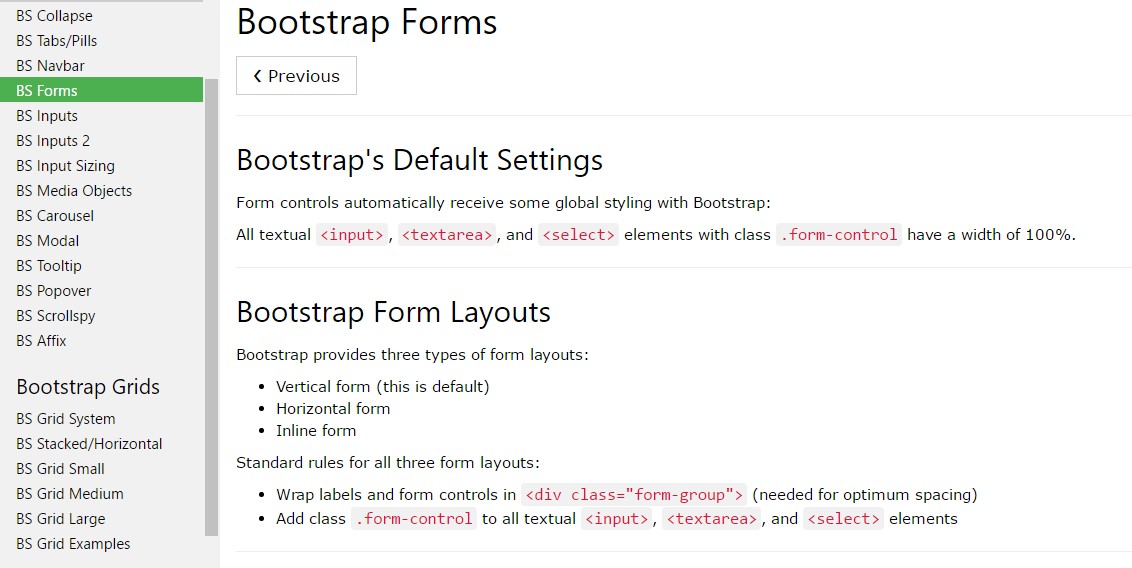
Considering that Bootstrap employs display: block and width :100% to most of our form controls, forms will by default stack vertically. Additional classes can possibly be used to vary this layout on a per-form basis.
Form categories
The .form-group class is the most convenient method to put in some building to forms. Its main purpose is to supply margin-bottom around a label and deal with coupling. Just as a bonus, since it's a class you can easily make use of it using <fieldset>-s, <div>-s, or else nearly some other component.

<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput">Example label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput" placeholder="Example input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput2">Another label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput2" placeholder="Another input">
</div>
</form>Inline forms
Employ the .form-inline class to present a number of labels, form managements , plus switches regarding a single horizontal row. Form controls inside of inline forms vary a little from their default states.
- Controls are display: flex, collapsing all HTML white colored territory and permitting you to provide placement control with spacing and also flexbox utilities.
- Controls and also input groups obtain width: auto to defeat the Bootstrap default width: 100%.
- Controls only show up inline within viewports which are at least 576px wide to account for small viewports on mobile devices.
You may likely need to manually deal with the width and placement of individual form controls together with spacing utilities (as demonstrated here) And finally, don't forget to constantly feature a <label> together with each form control, even though you need to cover it directly from non-screenreader site visitors with a code.
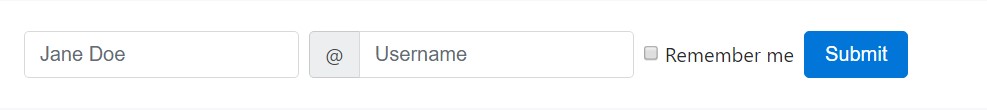
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInput">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormInput" placeholder="Jane Doe">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInputGroup">Username</label>
<div class="input-group mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<div class="input-group-addon">@</div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="inlineFormInputGroup" placeholder="Username">
</div>
<div class="form-check mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Remember me
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Custom-made form controls and selects are likewise maintained.
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="mr-sm-2" for="inlineFormCustomSelect">Preference</label>
<select class="custom-select mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormCustomSelect">
<option selected>Choose...</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Remember my preference</span>
</label>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Alternatives to concealed labels
Assistive technologies just like screen readers will likely have trouble with your forms if you don't involve a label for each input. For these inline forms, you can surely cover up the labels using the .sr-only class. There are actually extra different options of presenting a label for assistive modern technologies, such as the aria-label, aria-labelledby or title attribute. If not any of these exist, assistive technologies can resort to utilizing the placeholder attribute, in the case that present, yet consider that utilization of placeholder considering that a replacing for various other labelling solutions is definitely not recommended.
Utilizing the Grid
For extra organised form layouts that are additionally responsive, you can surely make use of Bootstrap's predefined grid classes or else mixins to develop horizontal forms. Provide the .row class to form groups and apply the .col-*-* classes to define the width of your labels and controls.
Be sure to add .col-form-label to your <label>-s as well so they’re vertically centered with their associated form controls. For <legend> elements, you can use .col-form-legend to make them appear similar to regular <label> elements.
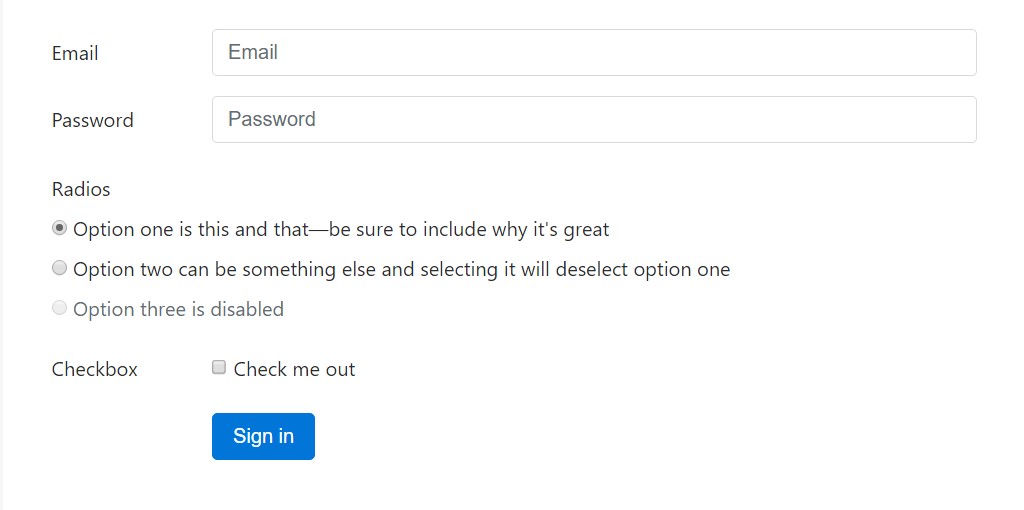
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="inputEmail3" placeholder="Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group row">
<legend class="col-form-legend col-sm-2">Radios</legend>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2">Checkbox</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Check me out
</label>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="offset-sm-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Sign in</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Grid-based form design and styles additionally support small-sized and large inputs.
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="lgFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-lg">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-lg" id="lgFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="smFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-sm">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-sm" id="smFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Checkboxes and radios
Default checkboxes and radios are greatly enhanced upon with the aid of .form-check, a specific class for each input types that improves the layout and behaviour of their HTML components. Checkboxes are for choosing one or else several options in a list, while at the same time radios are for picking one option from several.
Disabled checkboxes and radios are assisted, however, to supply a not-allowed cursor on hover of the parent <label>, you'll have to incorporate the .disabled class to the parent .form-check. The disabled class is going to additionally lighten the text message color to help reveal the input's state.
Each checkbox and radio is wrapped inside a <label> for three good reasons:
- It supplies a larger hit areas for checking the control.
- It delivers a handy and semantic wrapper to assist us removed and replace the default <input>-s.
- It produces the state of the <input> quickly, indicating no JavaScript is needed.
We cover the default <input> plus opacity and apply the .custom-control-indicator to develop a new custom form indicator in its place. Unluckily we just can't develop a custom-made one because of just the <input> considering that CSS's content doesn't function on that feature..
We employ the sibling selector (~) for every our <input> states-- just like : checked-- to correctly format our custom made form indicator . When incorporated with the .custom-control-description class, we can also format the content for each and every item built upon the <input>-s state.
In the checked states, we use base64 embedded SVG icons from Open Iconic. This provides us the best control for styling and positioning across browsers and devices.
Checkboxes

<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>Customized checkboxes can additionally use the : indeterminate pseudo class once manually established by using JavaScript (there is definitely no attainable HTML attribute for defining it).

In the case that you're utilizing jQuery, something like this should really suffice:
$('.your-checkbox').prop('indeterminate', true)Radios

<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio1" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio2" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>Default (stacked)
By default, any number of checkboxes and radios which are really close relative will be vertically piled as well as appropriately spaced by using .form-check.
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="">
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="" disabled>
Option two is disabled
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>Inline
Group checkboxes as well as radios on the identical horizontal row simply by adding .form-check-inline to any .form-check.

<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>Without labels
You should not possess a text message in the <label>, the input is positioned as you 'd look for. Right now strictly works with non-inline checkboxes and radios. Don't forget to still produce some form of label when it comes to assistive technologies (for instance, utilizing aria-label).

<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="blankCheckbox" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="blankRadio" id="blankRadio1" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>Static commands
If you need to apply plain content next to a form label within a form, utilize the .form-control-static class for an element of your choice.
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
</form>
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="sr-only">Email</label>
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
<div class="form-group mx-sm-3">
<label for="inputPassword2" class="sr-only">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword2" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Confirm identity</button>
</form>Disabled forms
Include the disabled boolean attribute for an input to avoid user interactions. Disabled inputs show up lighter and also put in a not-allowed cursor.
<input class="form-control" id="disabledInput" type="text" placeholder="Disabled input here..." disabled>Bring in the disabled attribute to a <fieldset> to disable all of the commands within.

<form>
<fieldset disabled>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledTextInput">Disabled input</label>
<input type="text" id="disabledTextInput" class="form-control" placeholder="Disabled input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledSelect">Disabled select menu</label>
<select id="disabledSelect" class="form-control">
<option>Disabled select</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label>
<input type="checkbox"> Can't check this
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</fieldset>
</form>Caveat concerning hyperlink features of <a>
By default, internet browsers are going to handle all of the original form controls (<input>, <select> plus <button> features) within a <fieldset disabled> as disabled, evading each of the key board and mouse interplays on all of them. But, in the case that your form also features <a ... class="btn btn-*"> features, these are going to simply be provided a format of pointer-events: none. Just as considered in the part about disabled state for buttons (and esspecially in the sub-section for anchor aspects ), this CSS feature is not actually yet standardised and isn't actually entirely maintained in Opera 18 and below, or else in Internet Explorer 11, and will not keep keyboard users from having the opportunity to focus or else trigger these hyperlinks. And so to remain safe, apply custom JavaScript to turn off such hyperlinks.
Cross-browser compatibility
Though Bootstrap is going to add these kinds of formats within all of the internet browsers, Internet Explorer 11 and below do not totally maintain the disabled attribute on a <fieldset>. Utilize custom JavaScript to disable the fieldset in all of these browsers.
Read-only inputs
Provide the readonly boolean attribute upon an input to avoid changes of the input's value. Read-only inputs seem lighter ( similar to disabled inputs), however hold the basic pointer.

<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Readonly input here…" readonly>Control scale
Determine heights utilizing classes like .form-control-lg, and put widths applying grid column classes just like .col-lg-*.
<input class="form-control form-control-lg" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-lg">
<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Default input">
<input class="form-control form-control-sm" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-sm">
<select class="form-control form-control-lg">
<option>Large select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control">
<option>Default select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control form-control-sm">
<option>Small select</option>
</select>Column size
Wrap inputs within a grid columns, or else any custom made parent feature, to effectively execute the desired widths.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-2">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-2">
</div>
<div class="col-3">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-3">
</div>
<div class="col-4">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-4">
</div>
</div>Assist content
The .help-block class is lost in the new version. If you require to apply a bit of added text to assist your visitors to much better navigate - employ the .form-text class instead. Bootstrap 4 has some construction within validation styles for the form controls being applied . In this particular version the .has-feedback class has been simply lost-- it is definitely no more required with the introduction of the .form-control-danger, .form-control-warning and .form-control-success classes adding a small-sized information icon straight inside the input areas.
Affiliating support message along with form controls
Assistance message must be clearly connected with the form control it relates to utilizing the aria-describedby attribute. This will definitely guarantee that the assistive technologies-- such as screen readers-- will reveal this assistance text when the user focuses or gets in the control.
Block level
Block support content-- for below inputs or else for longer words of the help content-- can possibly be conveniently achieved by using .form-text. This specific class includes display: block plus incorporates a bit of top margin intended for convenient spacing from the inputs mentioned earlier.
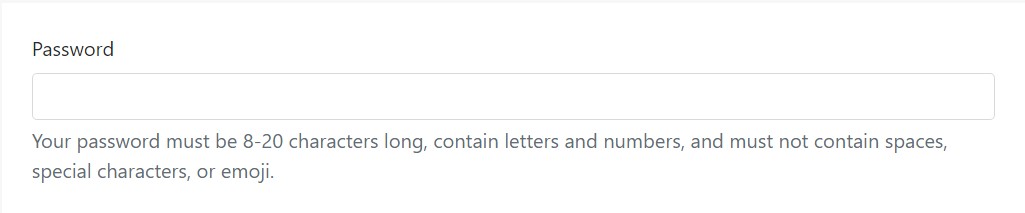
<label for="inputPassword5">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword5" class="form-control" aria-describedby="passwordHelpBlock">
<p id="passwordHelpBlock" class="form-text text-muted">
Your password must be 8-20 characters long, contain letters and numbers, and must not contain spaces, special characters, or emoji.
</p>Inline
Inline words have the ability to utilize any typical inline HTML feature (be it a , <span>, or else something else).
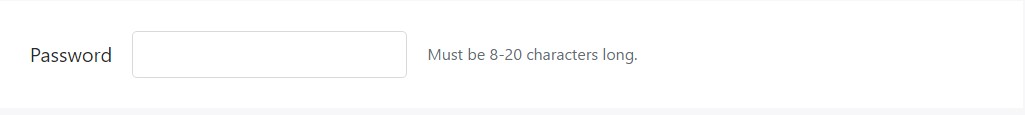
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword4">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword4" class="form-control mx-sm-3" aria-describedby="passwordHelpInline">
<small id="passwordHelpInline" class="text-muted">
Must be 8-20 characters long.
</small>
</div>
</form>Validation
Bootstrap provides validation formats for warning, success, and danger states on the majority of form controls.
The way to utilize
Here's a run-through of specifically how they perform:
- To employ, bring in .has-warning, .has-danger, or .has-success to the parent element. Any type of .col-form-label, .form-control, as well as custom made form element will acquire the validation formats.
- Contextual validation text message, along with your typical form field help message, may be incorporated along with the utilization of .form-control-feedback. This text is going to adapt to the parent .has-* class. By default it only features a little bit of margin for spacing also a changed color for every state.
- Validation icons are url()-s built via Sass variables that are applied to background-image announcements for every state.
- You can make use of your special base64 PNGs as well as SVGs by upgrading the Sass variables plus recompiling.
- Icons may also be disabled absolutely via preparing the variables to none as well as commenting out the source Sass.
Specifying states
Commonly saying, you'll need to use a specific state for specific types of feedback:
- Danger is ideal for the moment there's a blocking or possibly requested field. A user ought to write in this particular field correctly to provide the form.
- Warning performs well for input values that are in improvement, just like password strength, as well as soft validation just before a user attempts to submit a form.
- And lastly, success is perfect for cases as you have per-field validation throughout a form and want to encourage a user throughout the remaining fields.
Good examples
Here are some good examples of the aforementioned classes at work. First up is your basic left-aligned fields together with labels, guide text, and validation messaging.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputSuccess1">Input with success</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputSuccess1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputWarning1">Input with warning</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputWarning1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputDanger1">Input with danger</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputDanger1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>All those same states can also be taken together with horizontal forms.

<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row has-success">
<label for="inputHorizontalSuccess" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputHorizontalSuccess" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-warning">
<label for="inputHorizontalWarning" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputHorizontalWarning" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-danger">
<label for="inputHorizontalDnger" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputHorizontalDnger" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Checkboxes and radios are likewise assisted.

<div class="form-check has-success">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxSuccess" value="option1">
Checkbox with success
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-warning">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxWarning" value="option1">
Checkbox with warning
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-danger">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxDanger" value="option1">
Checkbox with danger
</label>
</div>Custom made forms
For even more modification plus cross browser consistency, make use of Bootstrap fully customized form features to substitute the web browser defaults. They're built on top of semantic and available markup, so they are really concrete replacements for any kind of default form control.
Disabled
Custom made radios and checkboxes are able to likewise be disabled . Provide the disabled boolean attribute to the <input> plus the custom indicator and also label explanation will be systematically designated.
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio3" name="radioDisabled" type="radio" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>Validation conditions
Add in the various other states to your custom made forms together with Bootstrap validation classes.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger mb-0">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>Stacked
Custom-made checkboxes and radios are inline to start. Provide a parent with class .custom-controls-stacked to assure each form control is on various lines.

<div class="custom-controls-stacked">
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked1" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked2" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>
</div>Select menu
Custom made <select> menus need to have just a custom-made class, .custom-select to produce the custom made styles.
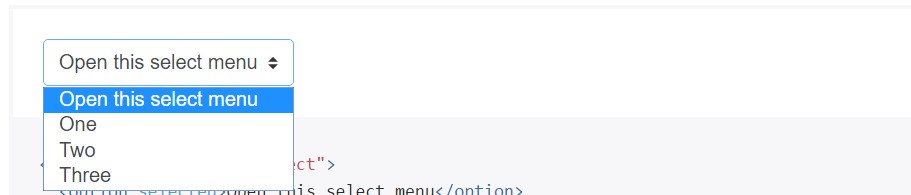
<select class="custom-select">
<option selected>Open this select menu</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>File web browser
The file input is the very most gnarly of the group and need additional JavaScript on the occasion that you would love to catch all of them up along with practical Choose file ... and selected file name message.
<label class="custom-file">
<input type="file" id="file" class="custom-file-input">
<span class="custom-file-control"></span>
</label>Here’s how to utilize:
- We wrap the <input> within a <label> therefore the customized control appropriately activates the file internet browser.
- We conceal the default file <input> via opacity.
- We apply : after to develop a custom background and directive (Choose file ...).
- We work with :before to create and position the Web browser button.
- We state a height upon the <input> for correct spacing for surrounding web content .
To puts it simply, it is really an entirely customized element, entirely developed using CSS.
Transposing or else modifying the sequences
The : lang() pseudo-class is utilized to permit simple translation of the "Browse" as well as "Choose file ..." message in additional languages. Simply override or bring in gates to the $ custom-file-text SCSS variable with the associated language emblem along with localized strings. The English strings may be individualized the same way. As an example, here's precisely how one might just include a Spanish interpretation (Spanish's language code is es)
$custom-file-text: (
placeholder: (
en: "Choose file...",
es: "Seleccionar archivo..."
),
button-label: (
en: "Browse",
es: "Navegar"
)
);You'll need to determine the language of your file (or subtree thereof) properly needed for the proper text message to be displayed. This can be accomplished applying the lang attribute as well as the Content-Language HTTP header, with some other methods.
Final thoughts
Fundamentally these are the brand-new components to the form components introduced within the current fourth edition of the Bootstrap framework. The overall impression is the classes got more user-friendly and specific for that reason-- much simpler to work with and having the custom-made control elements we can surely now get so much more expected appearance of the elements we incorporate in the web pages we create. And now all that is actually left for us is identify the right info we would definitely need from our possible site visitors to complete.
The best way to work with the Bootstrap forms:
Connected topics:
Bootstrap forms official documentation
Bootstrap guide
Support for Bootstrap Forms
Let us look over AMP project and AMP-form feature?